About the Digital Bible Library¶
The Digital Bible Library (DBL) is an online digital asset and licensing management platform developed and maintained by the United Bible Societies. The DBL gathers, validates, and safeguards digital scripture translation and publication assets from partnering agencies, and enables the managed licensing and distribution of these resources to other internal or external publishing partners.
The DBL is organized around the concept of archiving and licensing access to various entry types. The primary type being stored in DBL is a text entry, which contains the digital data for a scripture translation. Other entry types will contain the various products created from a translation text, such as print, audio, and epub. DBL maintains an internal relationship structure between text entries and the various related publication entries, and makes these publication relationships visible within its user interface.
DBL provides tools for archivists to gather project metadata, validate and upload data to the library, and an administration interface for each participating organization to manage their own activities within DBL.
What is stored in DBL?¶
DBL is both an archive and a licensing management environment. DBL text entries are stored in two distinct components - an ‘archive’ bundle, and a ‘release’ bundle. For example:
- A text archive bundle contains sufficient project data to allow completely reconstructing the source Paratext project instance which generated the DBL entry. The archive bundle is ‘private’, and is only accessible to the organization and their members responsible for ongoing maintenance of the text.
- A text release bundle contains scripture text, language, script, canon, versification, stylesheet reference, and other metadata organized in an efficient format for external publishing applications to ingest. The release bundle is ‘public’, in the sense that it is the package of data which may be securely released to external partners.
For details on the format of data stored in DBL, see: DBL Entry Reference
Organizations¶
DBL is primarily organized around the concept of organizations. A DBL organization may be either a content contributor (also called an IPC or “Intellectual Property Contributor”) or a publisher of content (also called an LCH or “Library Card Holder”). Assets in the library belong to contributing organizations and are released to publishing partner organizations through establishing a license agreement. Every organization in DBL is assigned one or more users who are given one or more operational roles. Roles are a category of permissions to perform certain types of functions within DBL.
For details on organization administration see: Managing Organizations.
Licensing Management¶
DBL provides an interface for contributing (IPC) organizations to add and maintain licensing documents, which can then be used for defining the terms for license agreements granted to publishing partners (LCHs). Approved LCH organizations are able to browse the DBL catalog and request access to specific content. DBL tracks and manages the agreement workflow, whether initiated by an IPC or LCH, and maintains an ongoing log of events and agreements between organizations.
For details on managing licensing documents, see: Managing Licensing Documents.
For details on the licensing workflow, see: Licensing Workflow Overview
Complete Workflow¶
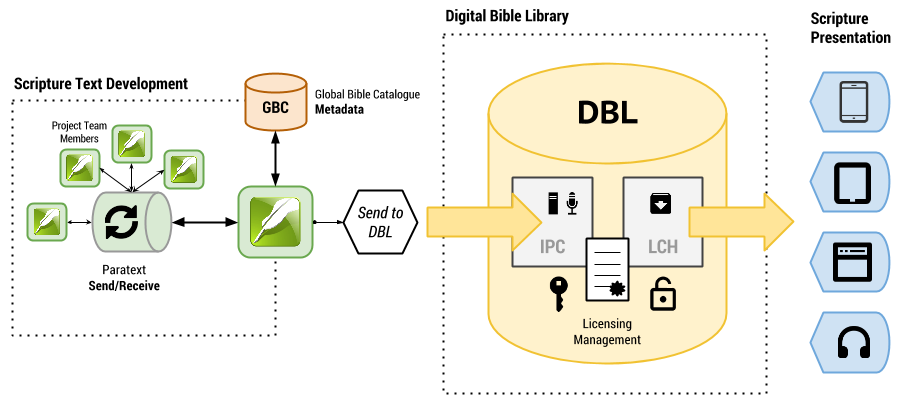
This diagram illustrates a complete DBL workflow for scripture text.
Archiving
- The translation team develops the scripture text, working in Paratext and sharing project data among members via the Send/Receive system.
- The Global Bible Catalog (GBC) contains an entry for project metadata.
- An organization member with archivist role uses various Paratext checking tools to test and validate various aspects of the project data.
- The archivist uses the Paratext DBL uploader to package the project text, and the metadata from GBC, and submits it to DBL.
Licensing and Publication
- The DBL administration interface is used by the IPC to establish a license agreement with an LCH publishing partner.
- When an agreement is established, the scripture translation is made available for download via the web interface or the API.
- The scripture text is presented on the LCH’s publishing system.